Benefits of M7.0
Lithification
Once M7.0 & lime mixture is hydrated, reaction begins and will continue for many years. The compressive strength and flexural strength will continue to increase for a long time. This characteristic is one of the main reasons why many great ancient structures have lasted for over thousand years.
Increases compressive strength

The reaction between M7.0 and calcium hydroxide happens after the C3S and C2S in the cement begin to hydrate. At the early stage of curing, 30% M7.0 substituting Portland cement mixture is slightly lower than reference OPC compressive strength. As time goes by, M7.0 keeps on reacting with the calcium hydroxide produced by cement hydration and increasing the compressive strength by producing additional C-S-H.
- After 21 curing days, 30% M7.0 with 70% Portland cement mixture begins to exceed reference OPC in compressive strength.
- After 28 days, it exceeds reference OPC by about 15% and reaction keeps on until there is no free calcium hydroxide available in the mass the compressive strength exceeds the reference OPC by 30~40%.
Autogenous healing
The unique characteristic of M7.0 is its inherent ability to heal or re-cement cracks within the concrete by means of its continuation of reaction with the calcium hydroxide freed from the hydration of Portland cement. This autogenous healing mechanism mends the structures by filling up most of the gaps inside the hardened concrete matrix.
Reduced permeability and voids
The leaching of water-soluble calcium hydroxide produced by the hydration of Portland cement can be a significant contributor to the formation of voids. Also, the amount of water of convenience, used to make the concrete workable during the placing process, creates permeable voids in the hardened mass. M7.0 can react quickly with calcium hydroxide and form additional C-S-H. Thus, it not only prevents the water soluble compound from migration out of the concrete, but also makes the cement paste denser, with no voids. In addition, M7.0 can increase the fluidity of concrete without “water of convenience ". Therefore, the volume of capillary pores created by water can be minimized.
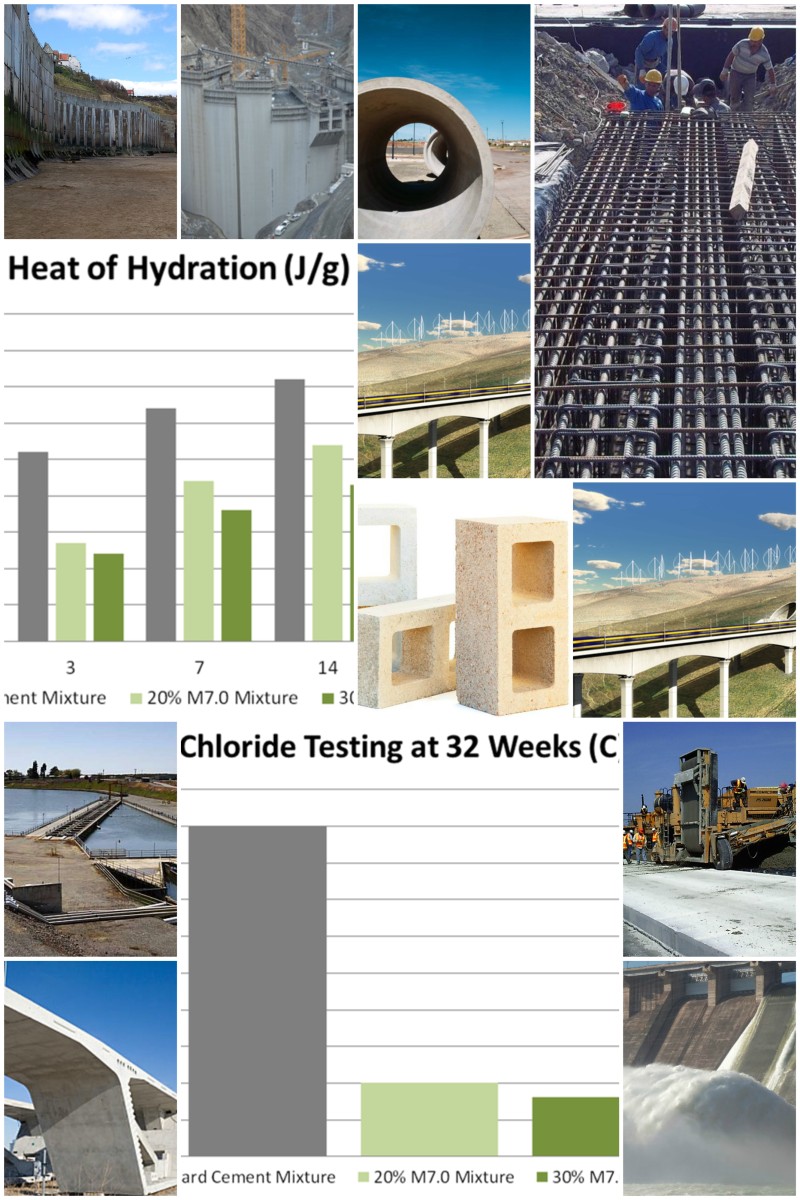
Reduces expansion and heat of hydration
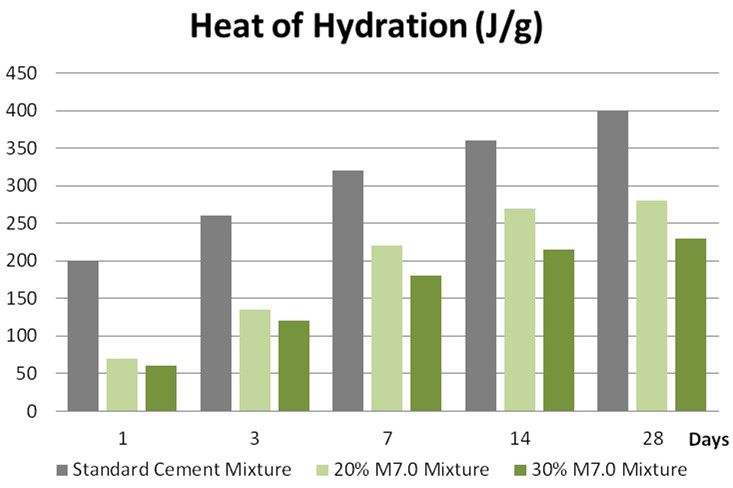
Experiments show that replacing 30% Portland cement with M7.0 can reduce the expansion and heat of hydration to as low as 40%. M7.0 decreases the heat generated by cement hydration and delays the time of peak temperature.
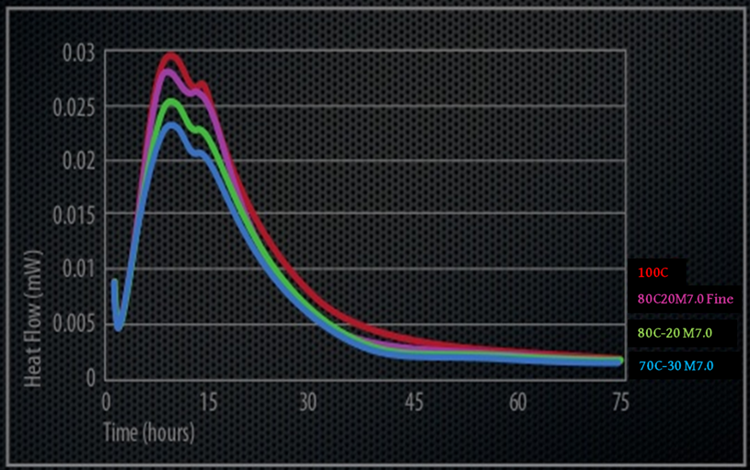
Reduces creep and cracks
While concrete is hardening, the water of convenience dries away. M7.0 moderates the expansion and shrinkage of concrete. It also helps to lower the water content of the fresh concrete. Therefore, the creep and cracks can be significantly reduced.
Fatigue Properties
All engineering materials are subject to potential failure caused by progressive fracture under the action of repeated loadings. The stress level (the ration of applied stress to the modulus of rupture) gradually decreases. The flexural strength of M7.0 & Portland cement mixture, like the compressive strength, increases with time. Its autogenous healing mechanism also helps to mend the fractures and recover the stress level.
Reduces micro-cracking
M7.0 & portland cement mixture expands shrinks moderately so there is no micro-cracking inside the C-S-H paste. In addition, the aggregate keeps close contact with the C-S-H paste after drying.
Increases resistance to chloride attack
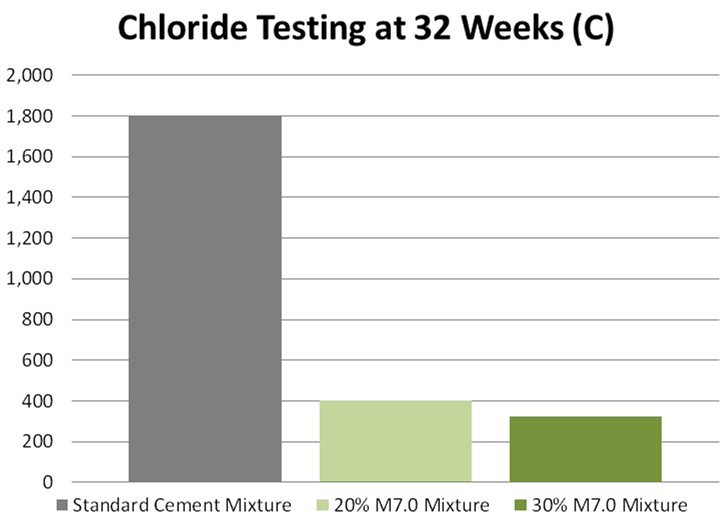
The 30% M7.0 added into cement can react with almost all the free calcium hydroxide and form a much denser paste. Thus, the penetration of chloride can be minimized and the few penetrated chloride ions cannot find free calcium hydroxide to react with. Concrete structures exposed to marine conditions must use M7.0 as a strengthening additive.
Increase resistance to sulfate attack
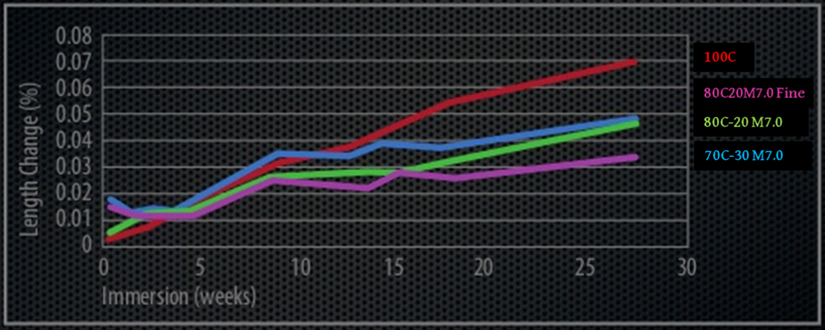
M7.0 contains virtually no sulfate in it and can quickly react with free calcium hydroxide to form additional C-S-H which makes the paste much denser. Therefore, it eliminates the formation of gypsum, ettringite and thaumasite. Experiments show that 20% substitution of Portland cement by M7.0 can reduce sulfate expansion by 80%.
Reduces alkali-aggregate reaction
Experiments show that only using 25% M7.0 to substitute OPC can reduce alkali-silica expansion by 70%. The alkalis in M7.0 are fixed in the glass phase. During cement hydration, M7.0 reacts with the freed calcium hydroxide and maintains the PH level in the paste. By trapping the alkalis inside the paste in the form of alkali-silica gel, the silica in M7.0 renders the alkalis in the Portland cement unavailable for reaction with aggregate.
Impedes Carbonation
Adding 30% M7.0 into Portland cement can enhance its resistance against carbonation. The concrete made from this mixture has virtually no micro-cracking to allow diffusion of carbon dioxide. Its paste has very low permeability and traps all the alkali in cement to form alkali-silica gel scattering within the glassy matrix, so that it prevents the alkali to act as a catalyst in cement carbonation.
Reduces freeze-thaw damage
Adding M7.0 into Portland cement can assist the concrete in resisting freeze/thaw damage by minimizing the permeability, voids, cracks induced by chemical expansion and attack. The paste made from M7.0 & Portland cement mixture is so dense and closely cohered with aggregate that moisture can hardly penetrate into its matrix.
Protects steel reinforcement from corrosion
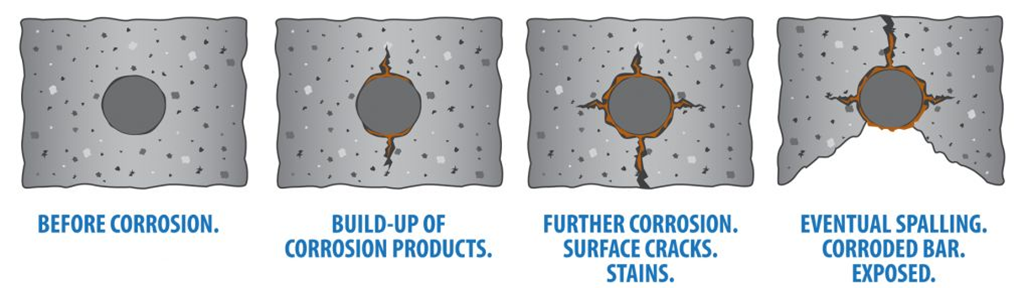
The concrete made from 30% M7.0 and 70% Portland cement mixture can protect steel reinforcement in a so densely sealed alkaline environment that no liquids and gases can penetrate through to cause corrosion to the steel.
Increases abrasion resistance
M7.0 increases the compressive strength of concrete and makes the concrete matrix denser and stronger. It also prevents the formation of pulpy, crispy or water soluble materials created by chemical attack.
Lowers water requirement with high fluidity, self-leveling and compression
30% M7.0 with Portland cement mixture can achieve high concrete fluidity with low w/c ratio. Thus, concrete can be self-leveled and self-compressed without the use of vibrator.
Improves durability
M7.0 contains no carbon and sulfur and is free from any contamination and therefore M7.0 compared to GGBFS and Fly-Ash guarantee a long life for the structures.
Unifies quality
Uniformity of cement quality is an important requirement for building large structures which can be met with M7.0. Most of the synthetic additives as GGBFS and Fly-Ash cannot meet this criterion.
Reduces carbon dioxide emission
The carbon dioxide emission by cement production is an environmental concern. Using M7.0 to substitute 30% Portland cement helps to solve the problem.
Reduces Costs
M7.0 is cheaper than Portland cement. Its characteristics of improving workability also help to save a lot of construction costs and manpower, such as vibration and water cooling.